Exchange Rate Regimes, Mundell - Advanced
UCLA - Econ 221 - Advanced Macro
François Geerolf
November 26, 2019
Types of Exchange Rate Regimes
Exchange Rate interventions
Many central banks intervene to influence exchange rates in floating exchange rate regimes. That’s called dirty floating.
Many developing and emerging markets peg to the dollar.
Krugman, Obstfeld, Melitz - International Economics
“Avoid damaging restrictions”

“Avoid damaging restrictions”

“Avoid damaging restrictions”

Effect of Permanent Fiscal Expansion
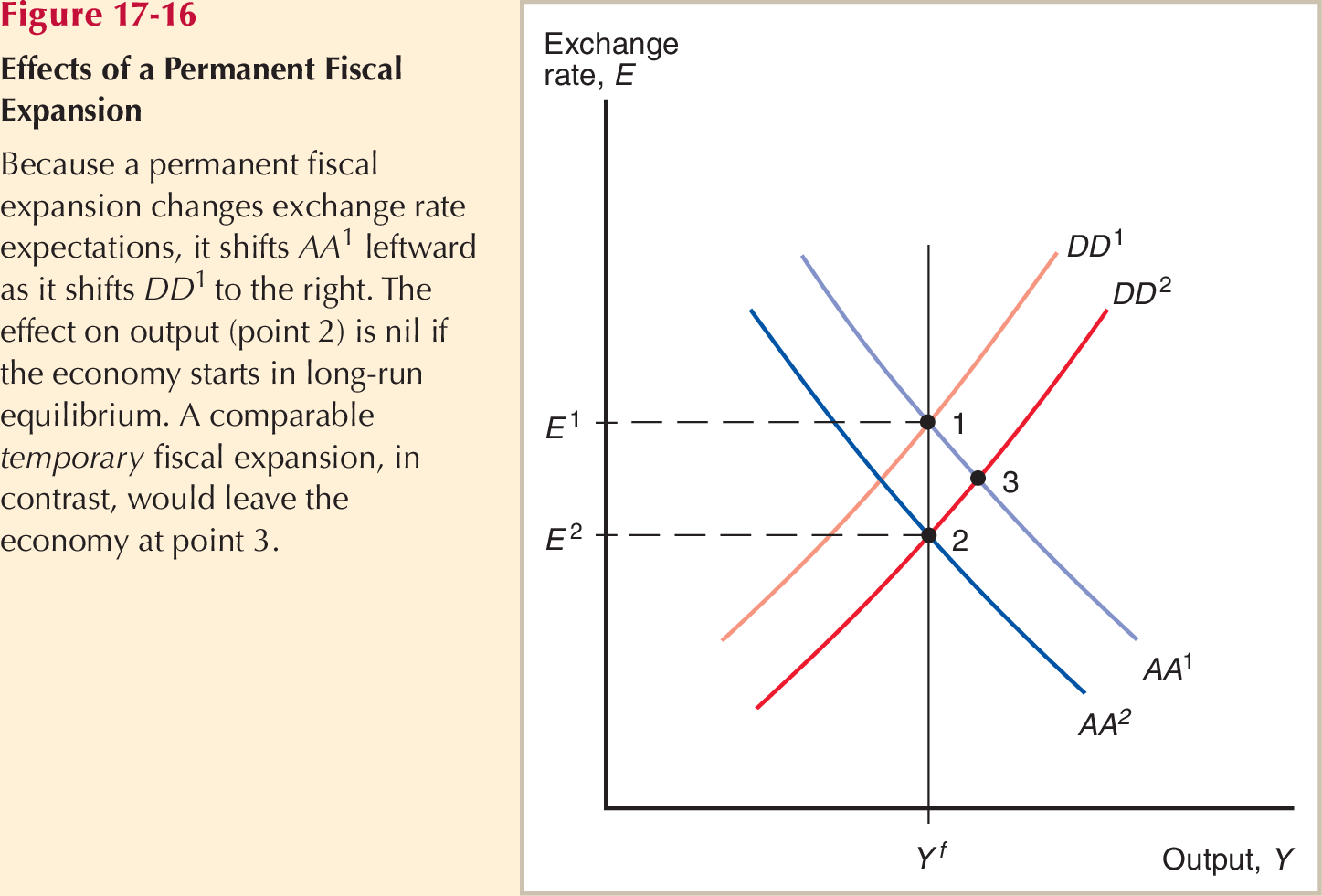
Fiscal Policy

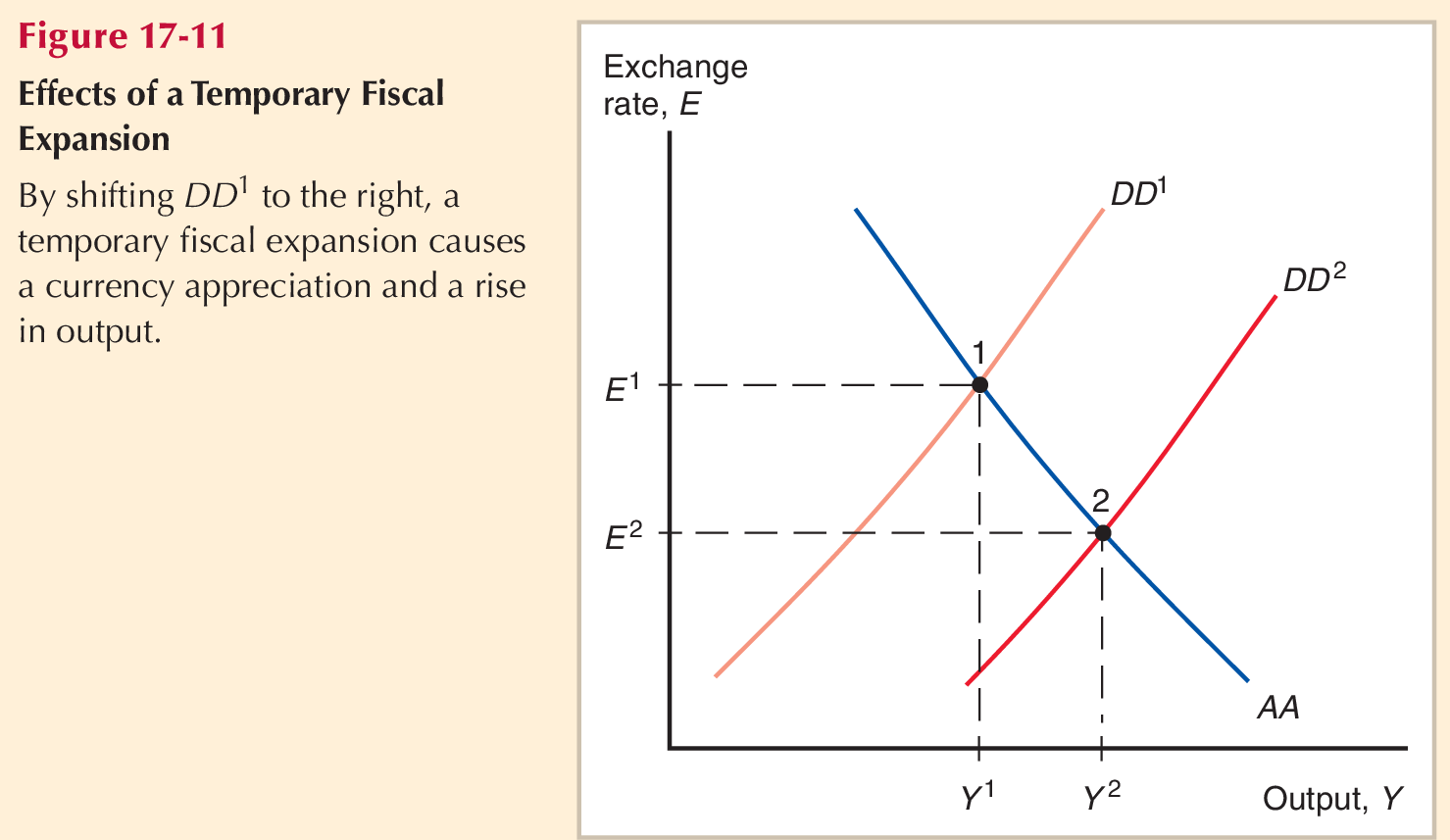
Temporary Fiscal Expansion
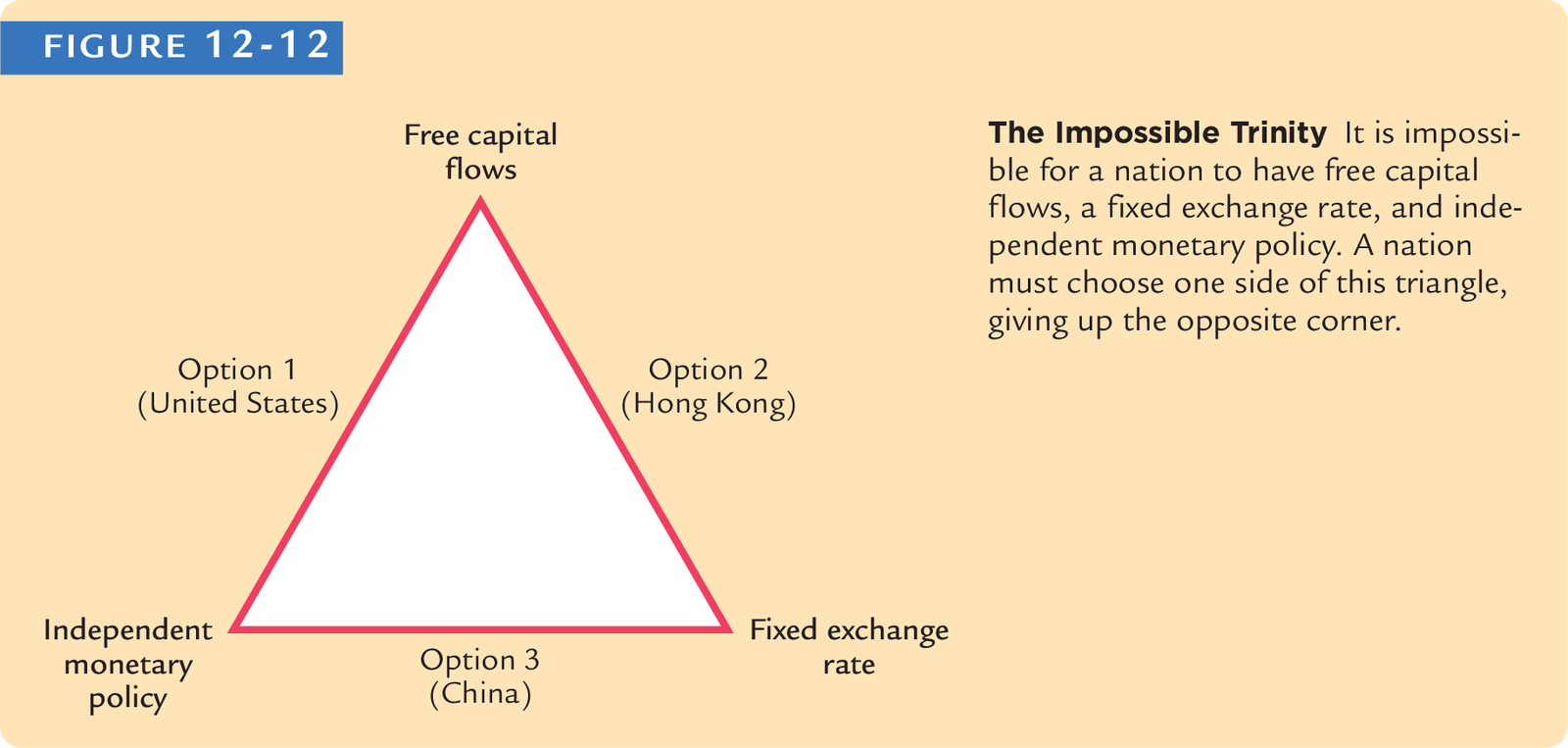
Impossible Trinity
Triangle
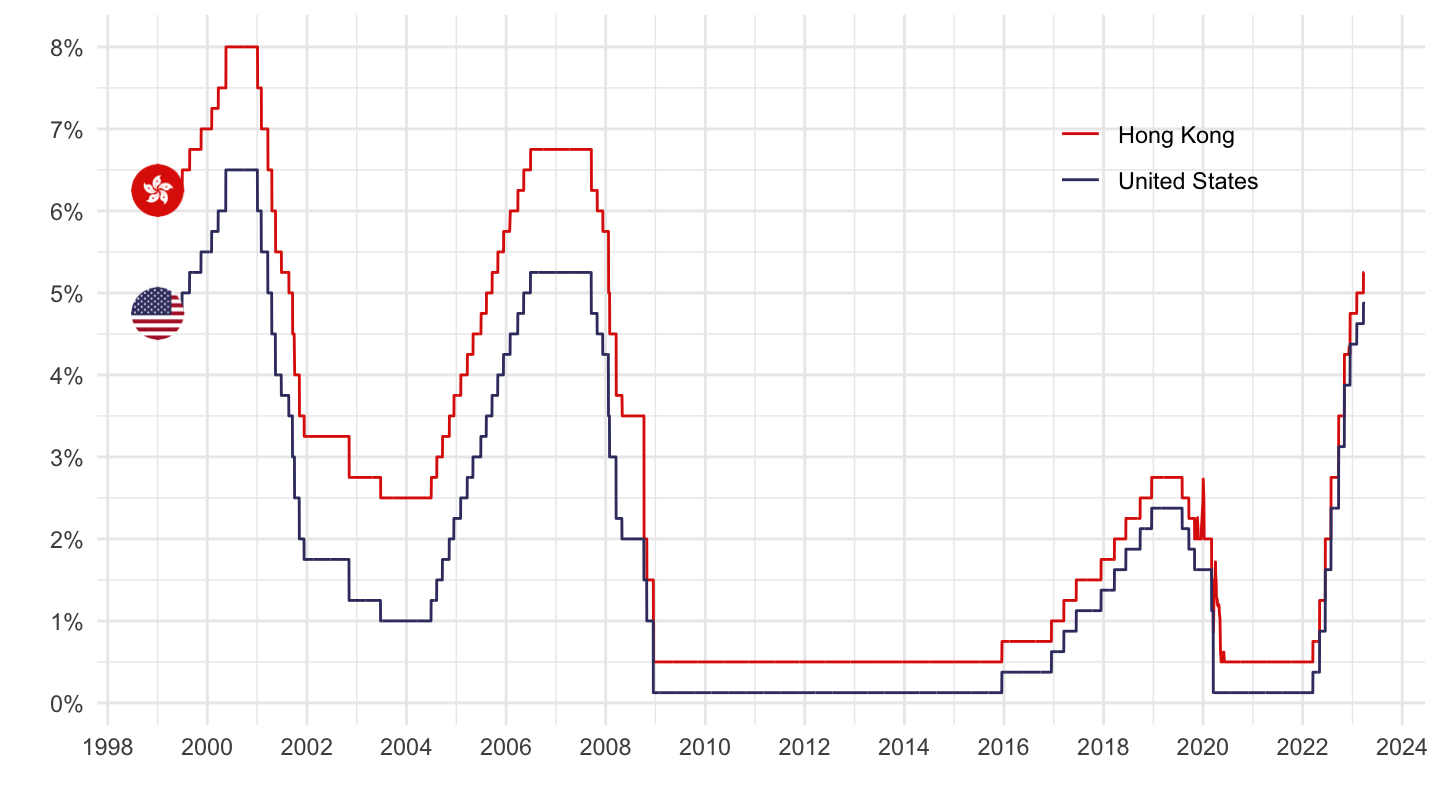
Example of Hong Kong
Undergraduate treatment of Mundell-Fleming
Purely theoretical

Euro - Expressed my doubts

Obstfeld-Rogoff

Obstfeld-Rogoff

(IS) curve with Net Exports
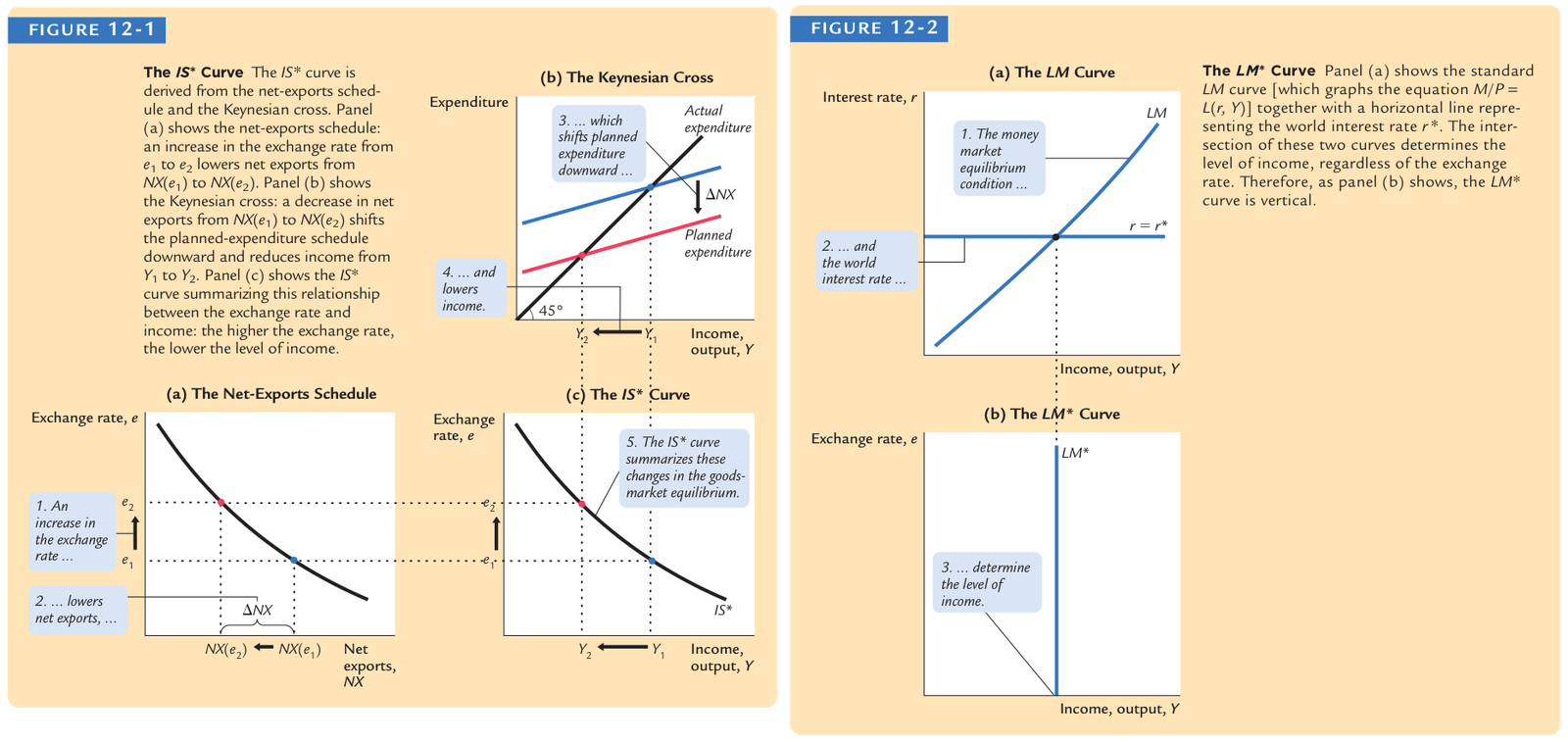
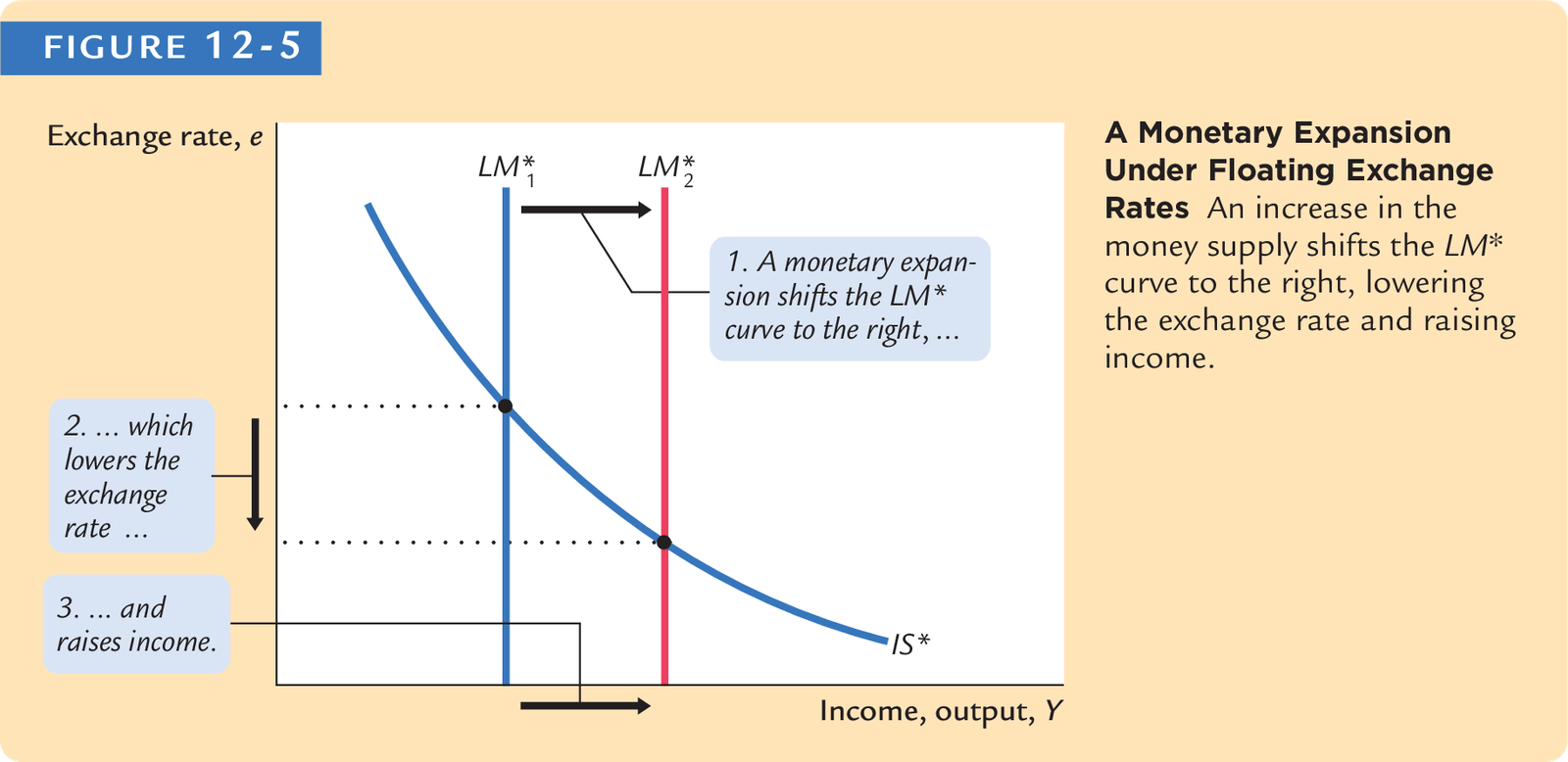
Mundell-Fleming Model
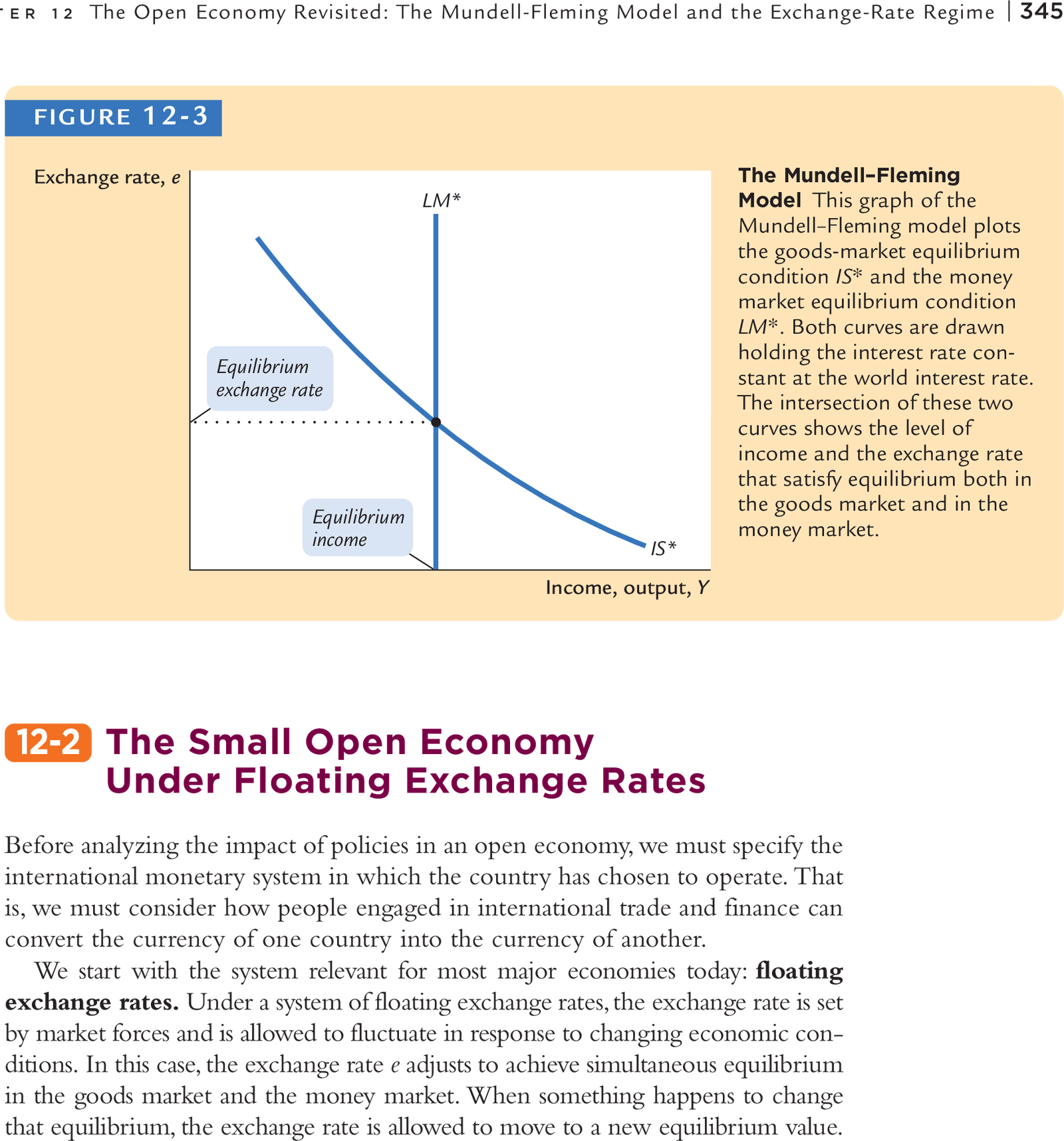
Floating Exchange Rates
Impossible Trinity

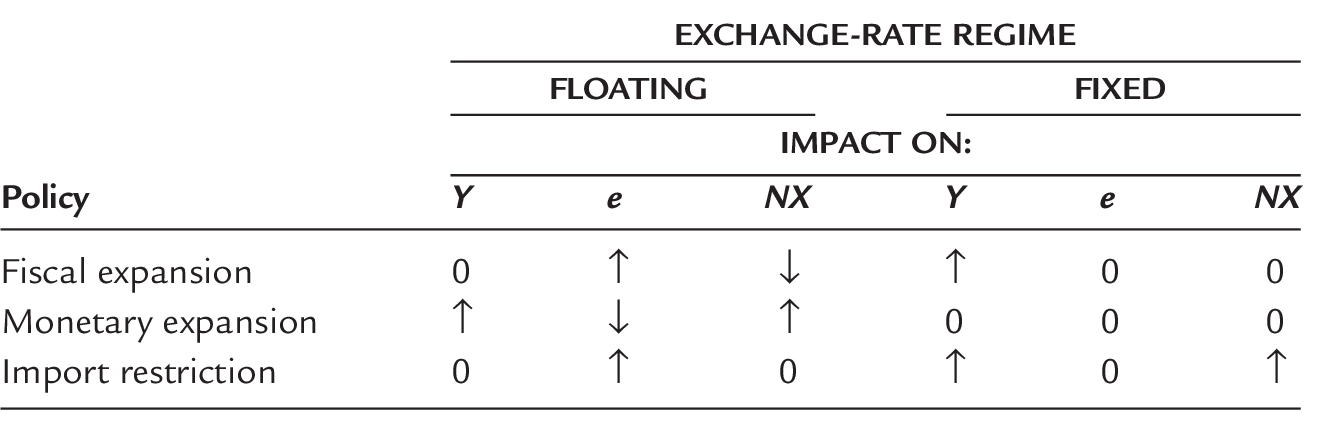
Summary of Policy Effects
Effect of tarriff
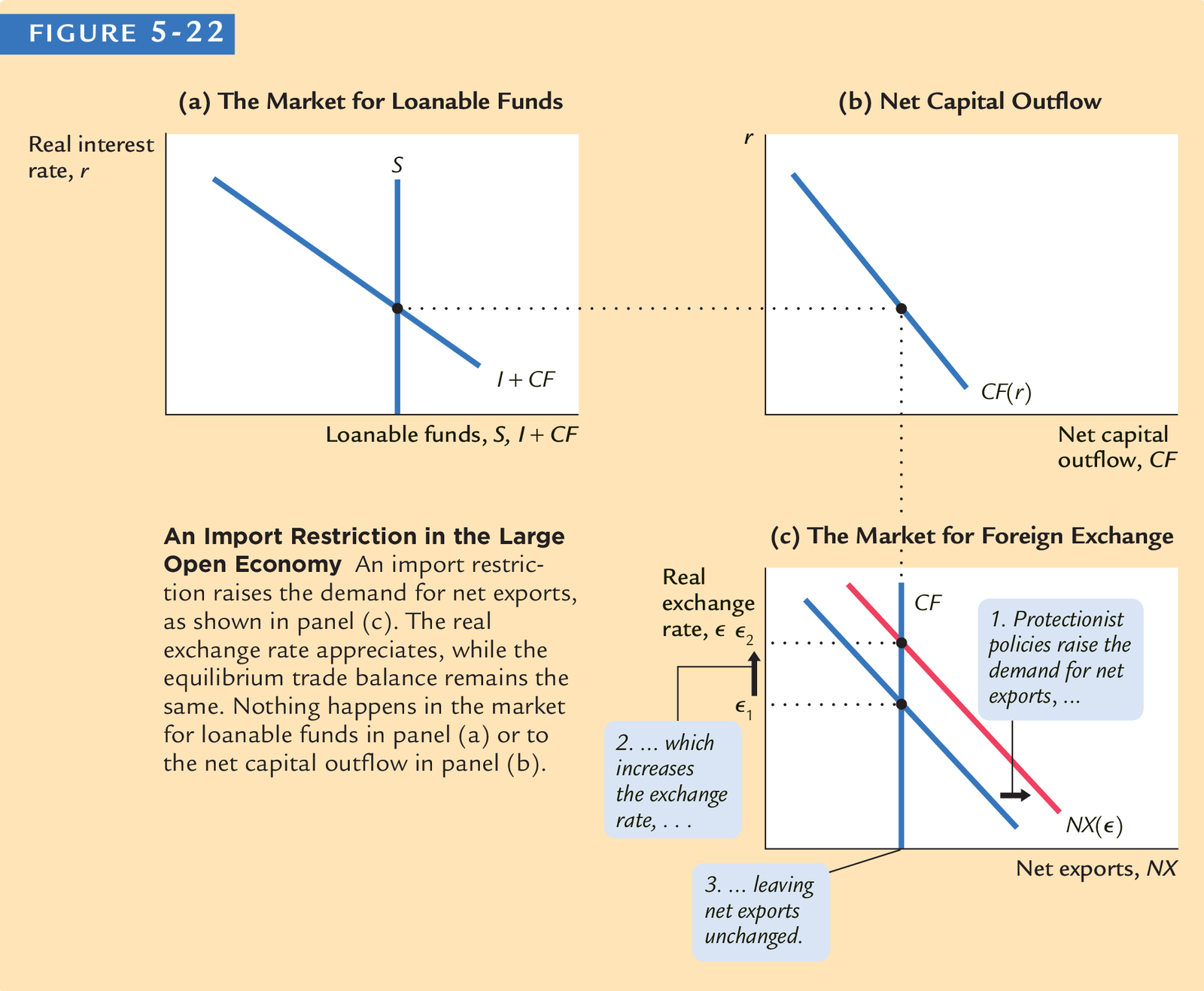
Mundell (1961a)
Balance-of-payments crises

Unemployment or depreciation

Mundell (1961b)
Article cited by Obstfeld against Trump

Article cited by Obstfeld against Trump

Title: Flexible Exchange Rates and Employment Policy

Mercantilist element in Keynesian Policies ?

Flexible exchange rates

Fiscal policy more efficient under fixed?
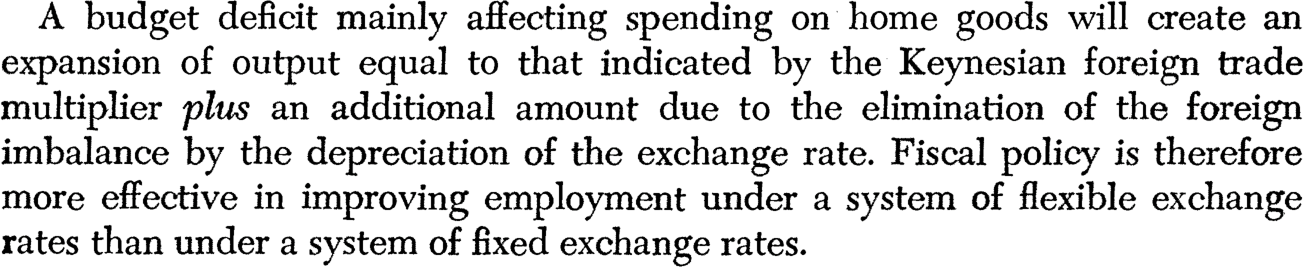
Mundell (1963)
Maury Obstfeld - Harry Johnson
Lecture
Maury Obstfeld
Countries would exploit flexible rates in order to gain competitive advantage.
President Trump has complained about Europe and other countries devaluing their currencies, and push for offsetting tarriffs.
The argument that Johnson made was that if countries had limited reserves, in the face of trade deficits they would be inclined to use protective measures in order to improve their positions.
As economists we don’t necessarily believe in that direct link between tariffs and the current account.
Economists usually focus on limited reserves, but how about perhaps even more importantly the issue of competitivevess (that is, even if you have )
Krugman (1990)
Capital mobility under Bretton Woods was driven.
1960s: measures that expanded the scope for long term capital movements.
Fixed Exchange Rates and Trade Deficits
Fixed Exchange Rates
1925: Return to Gold
Exchange Rate Flexibility is the worst currency systems except all others that have been tried.
IMF in Britain

Freeing Domestic Management

Johnson (1969)

Friedman
Limiting international payments.
In a modern world of high capital mobility.
Volume of international financial transaction is greater than that of trade transactions.
Eichengreen (1992)
Official position of Bank of France

France is alone

Blum: no conflict

Stickiness of wages and prices ?

Quasi Fixed Exchange Rates
Denmark (1997-2020)
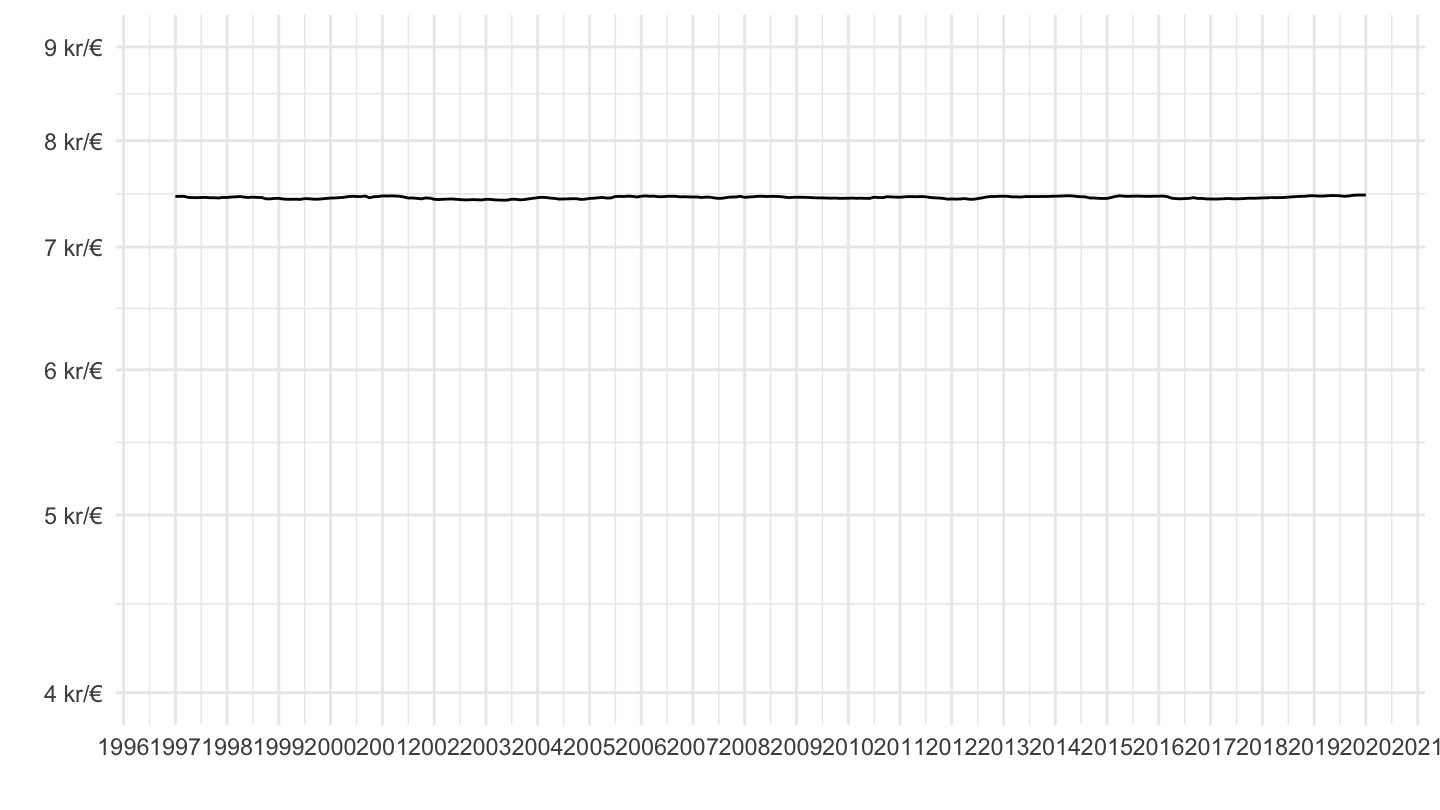
Denmark: Longer Period
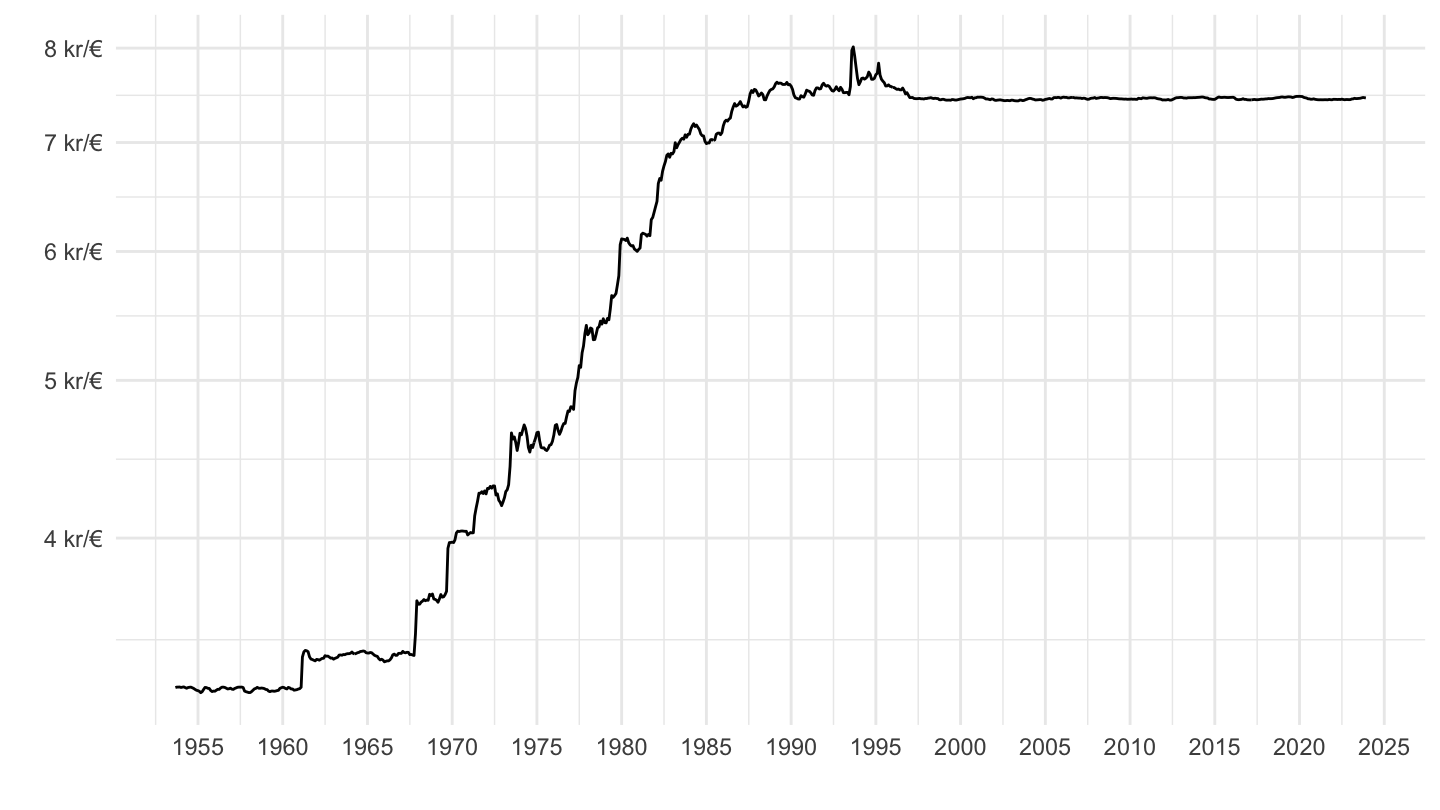
Denmark: Clearly not Pegging to Dollar
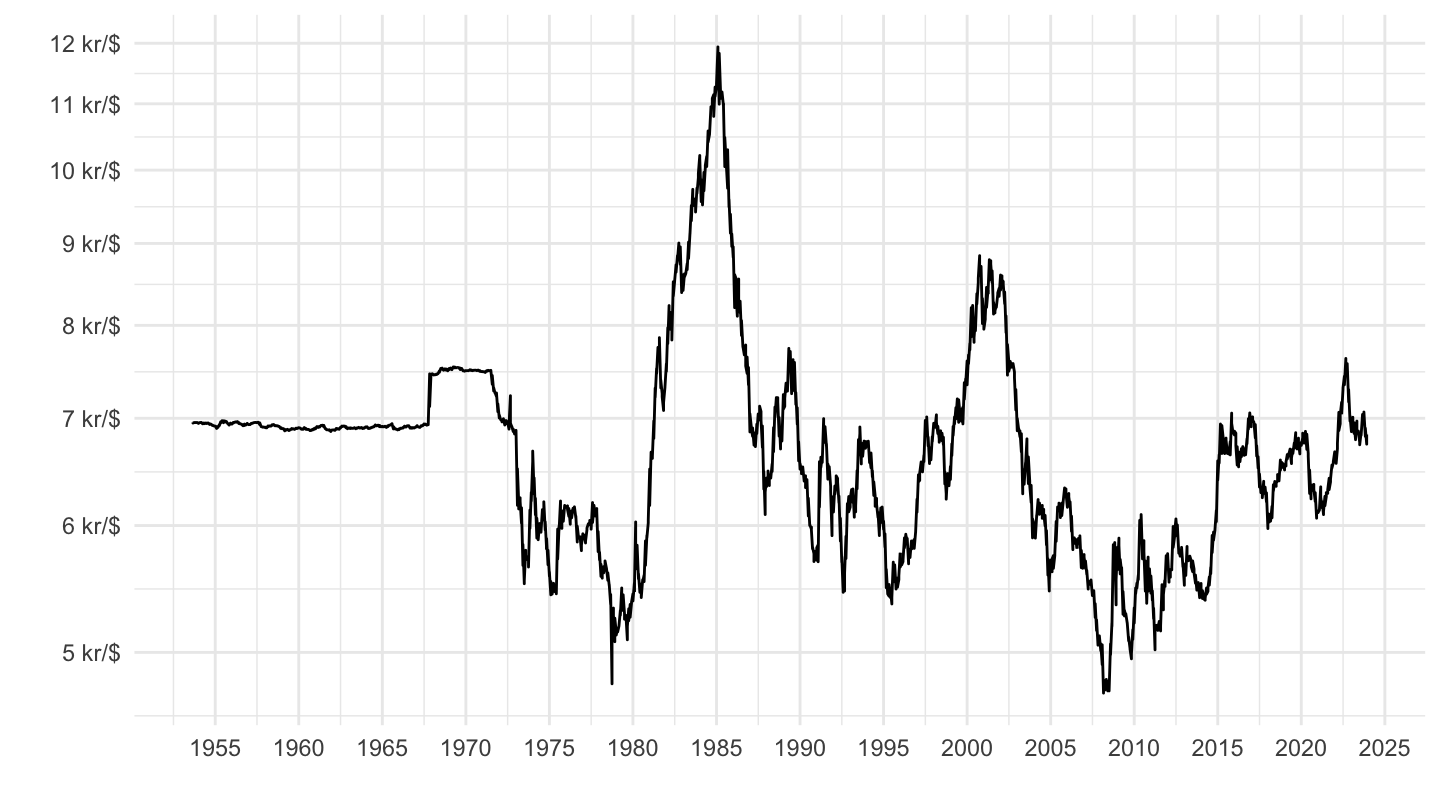
Complicated: the case of Switzerland
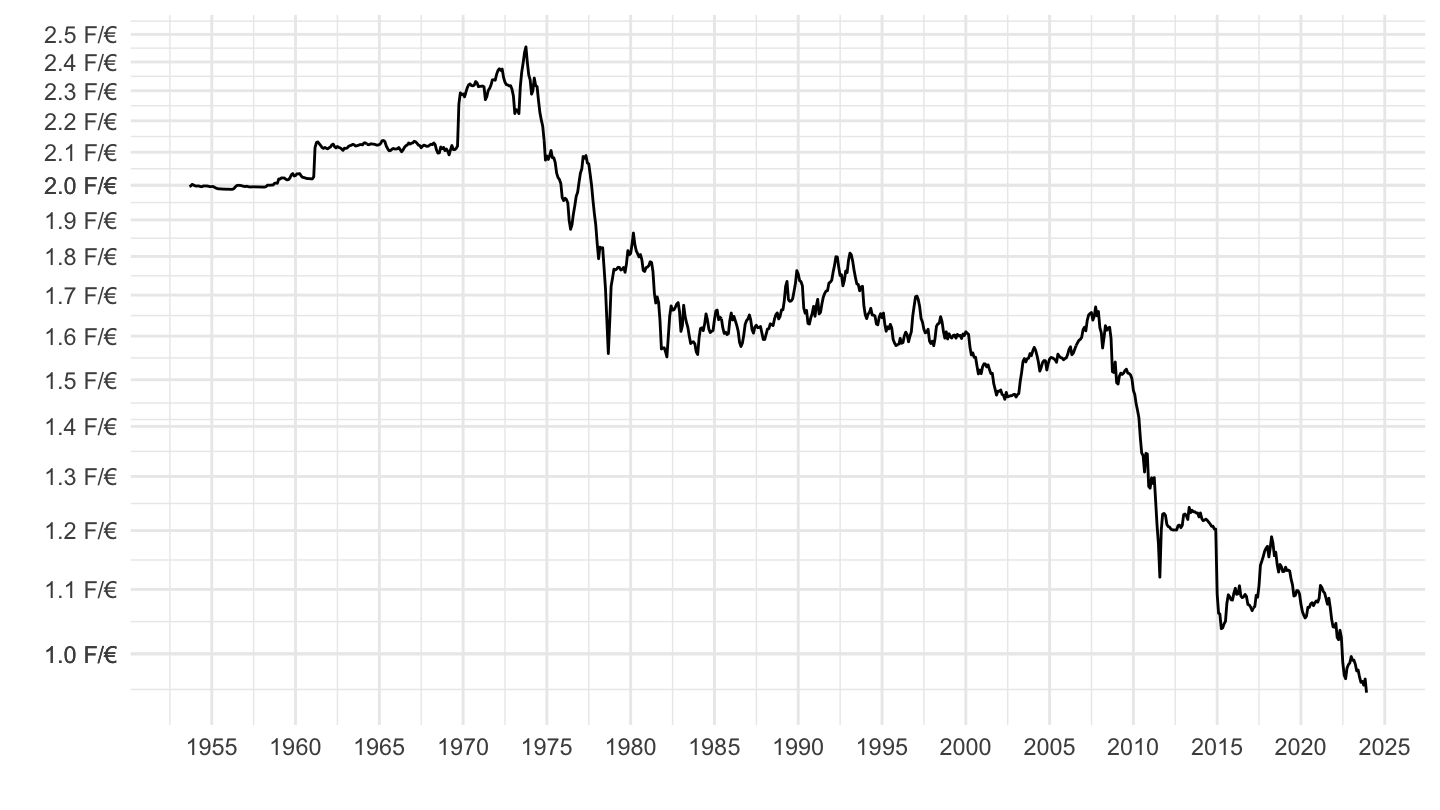
Based on Sticky Prices
As I told you, I do not believe in sticky prices very much.
Or at least, not in the way that New-Keynesians believe in sticky prices.
Rather, I believe that Keynesian effects come from an excess of savings over investment, and that’s my measure of slack.
Stimulus in Fixed VS in Flexible
WEO 2017-
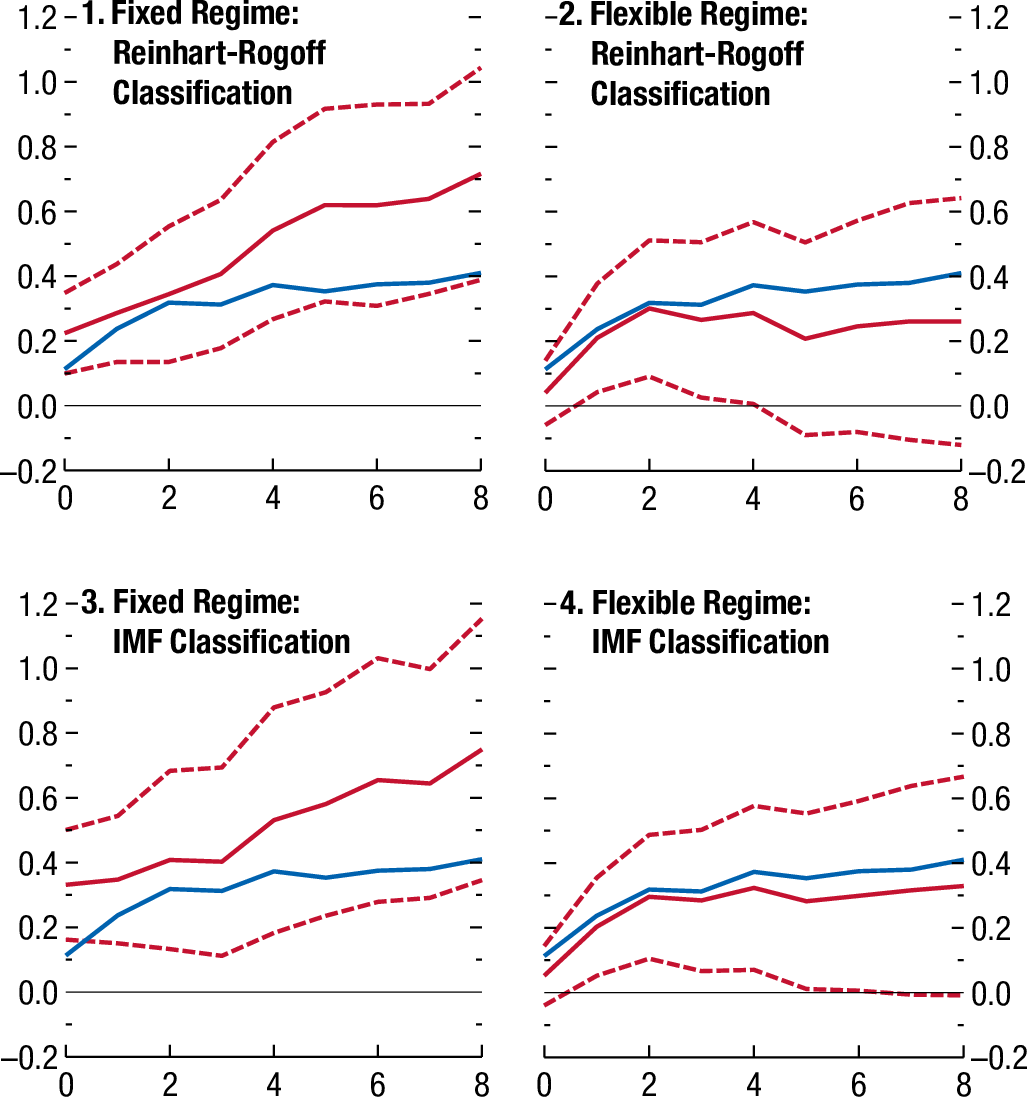
WEO 2017 - Empirical observations
More effects on the trade balance in fixed exchange rate regimes than in floating rate regimes.
Why do we think that is ?
One explanation could be that a devaluation due to an easing of monetary policy prior to stimulus acts like a “tarriff” prior to stimulation. Hence, goods from abroad are more expensive for local consumers.
Another could be that investors are less worried about exchange rate risk with fixed rates.
Guajardo, Leigh, Pescatori (2014)
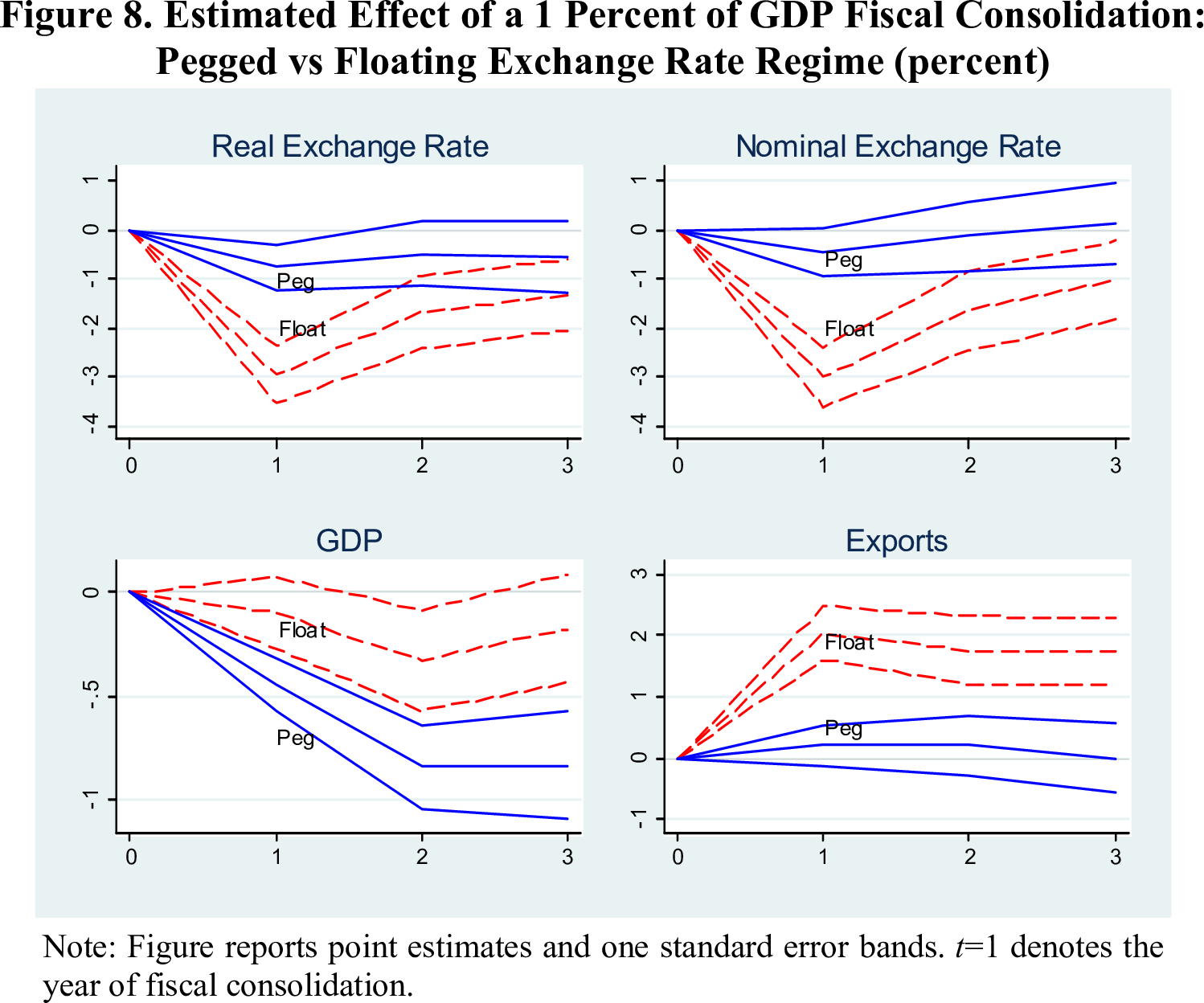
Phillips Curve Again
Differences

Phillips curve in fixed rates
I see this as another confirmation that the Phillips curve is valid only under fixed exchange rates.
Indeed, both positive supply shocks on the Traded Goods sector, as well as positive demand shocks in the non-traded goods sector leads to an appreciation in the real exchange rates, as well as diminished unemployment in a place.
At the same time, positive
U.S. Price Level
- Hoover Policy: raising Taxes to restore the balance in the budget. Deflation. 1933: Roosevelt leaves Gold Standard
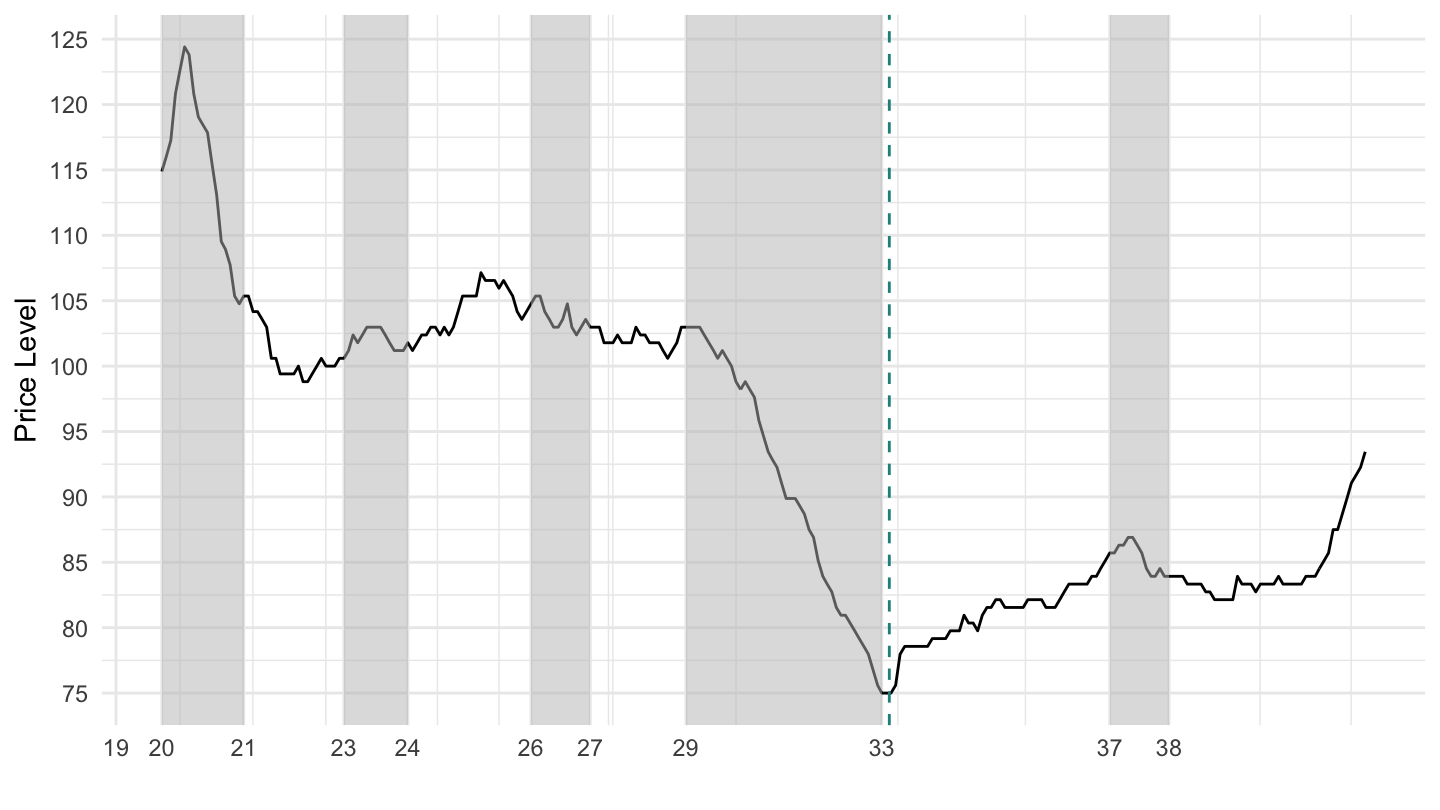
- In new Keynesian economics, the only difference
Map
Three generations of crisis
Krugman, 1979s
Prior to the collapse, the Mexican peso had been operating a fixed parity against the $US. However, leading up to the end of 1994, there were several underlying weaknesses in the Mexican economy which led speculators to question the sustainability of the peg. Including: (1) PPP calculations which indicated that prices/costs had risen in excess of trading partners, implying that the fixed exchange rate was overvalued. This was indicated as the cause of a growing current account deficit, which rose to 7% of GDP in 1993 and 8% in 1994.
2008–2011 Icelandic financial crisis
Iceland’s Bank
Instability in Iceland
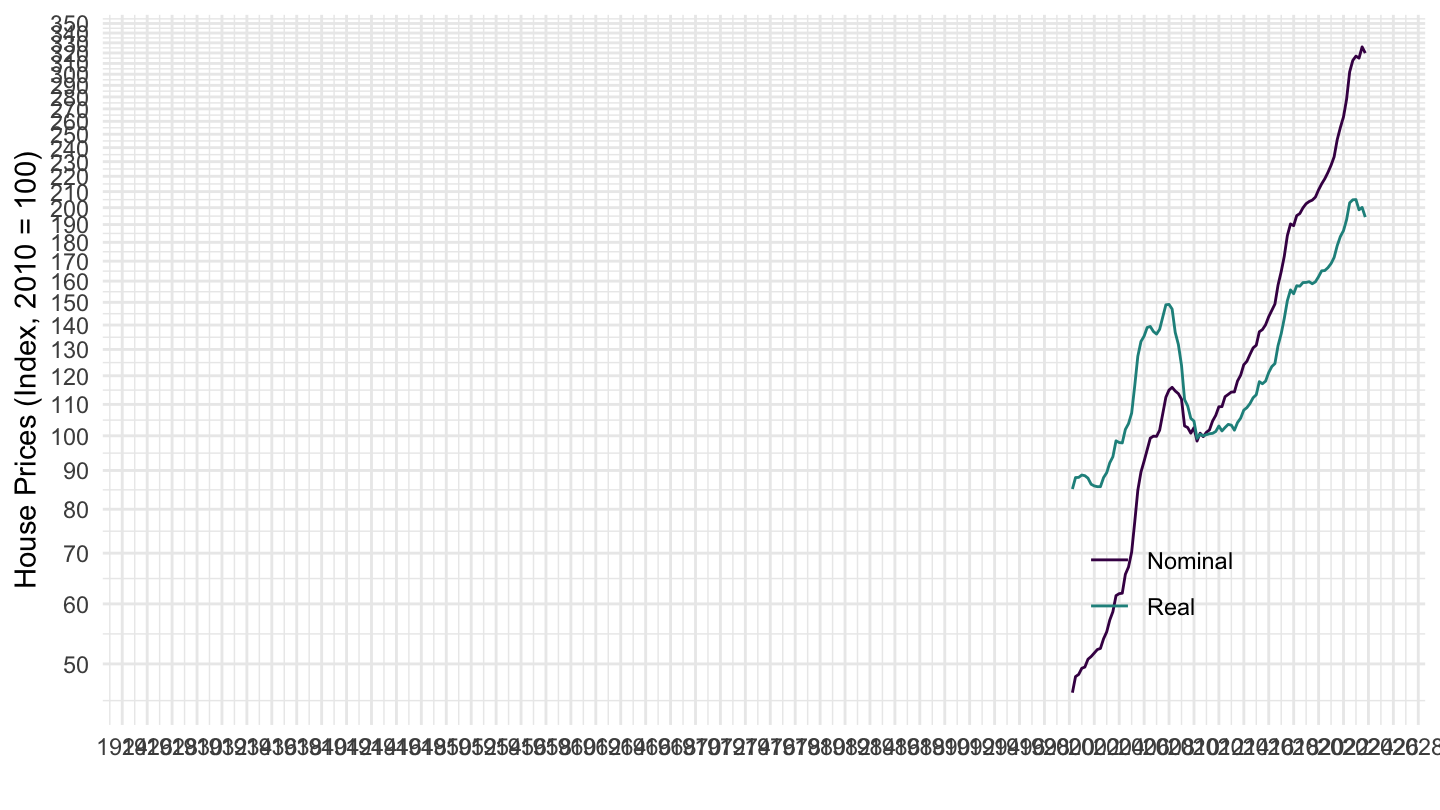
House Prices
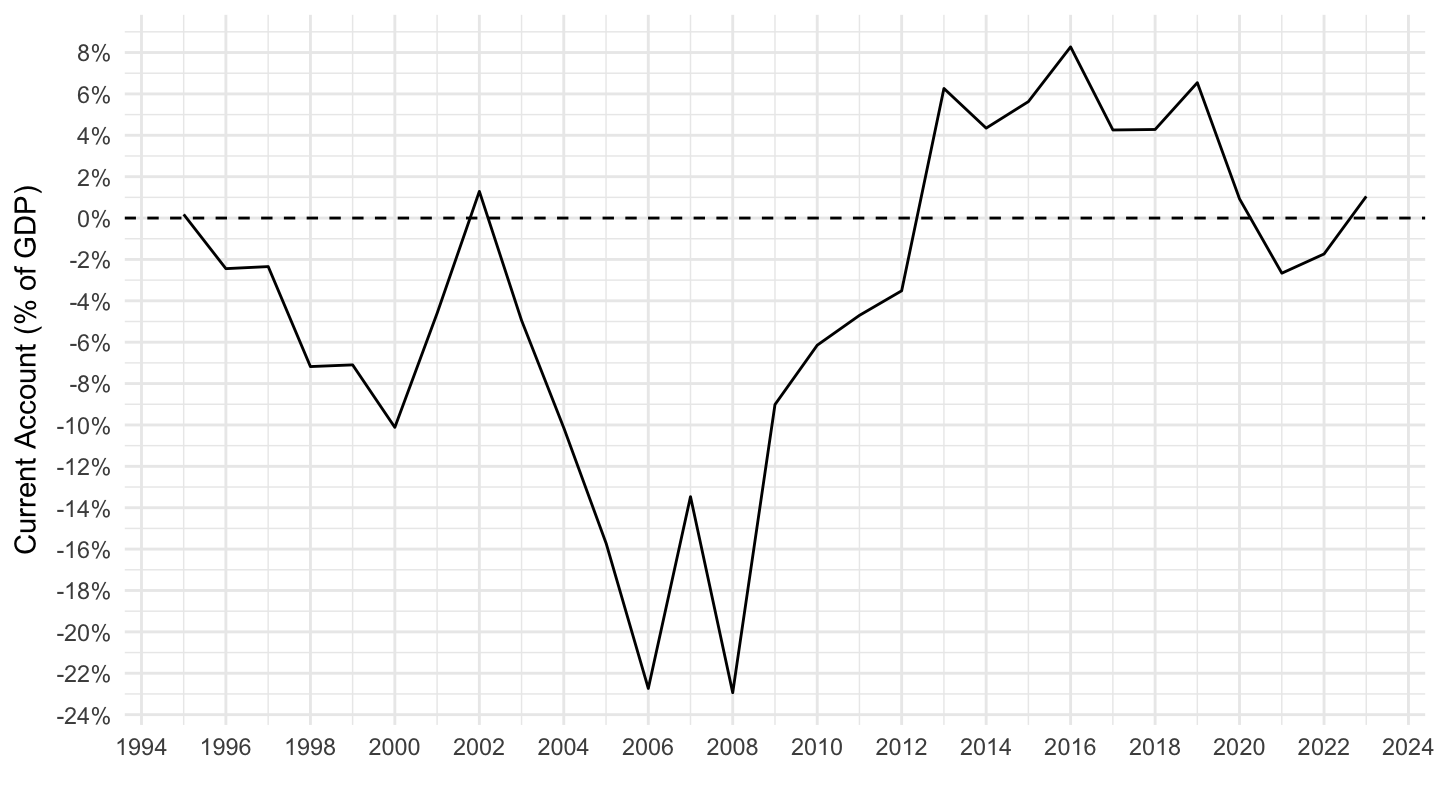
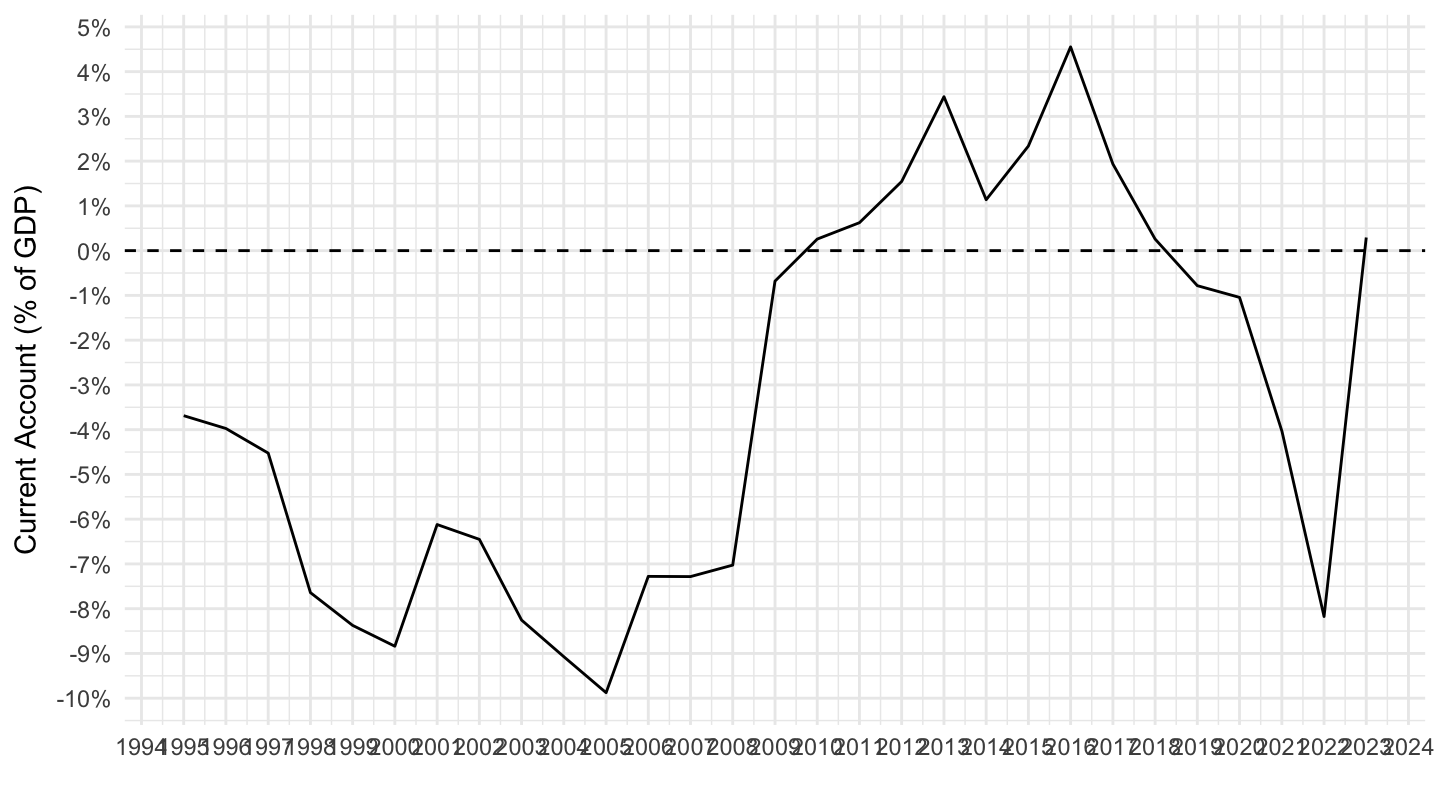
Current Account
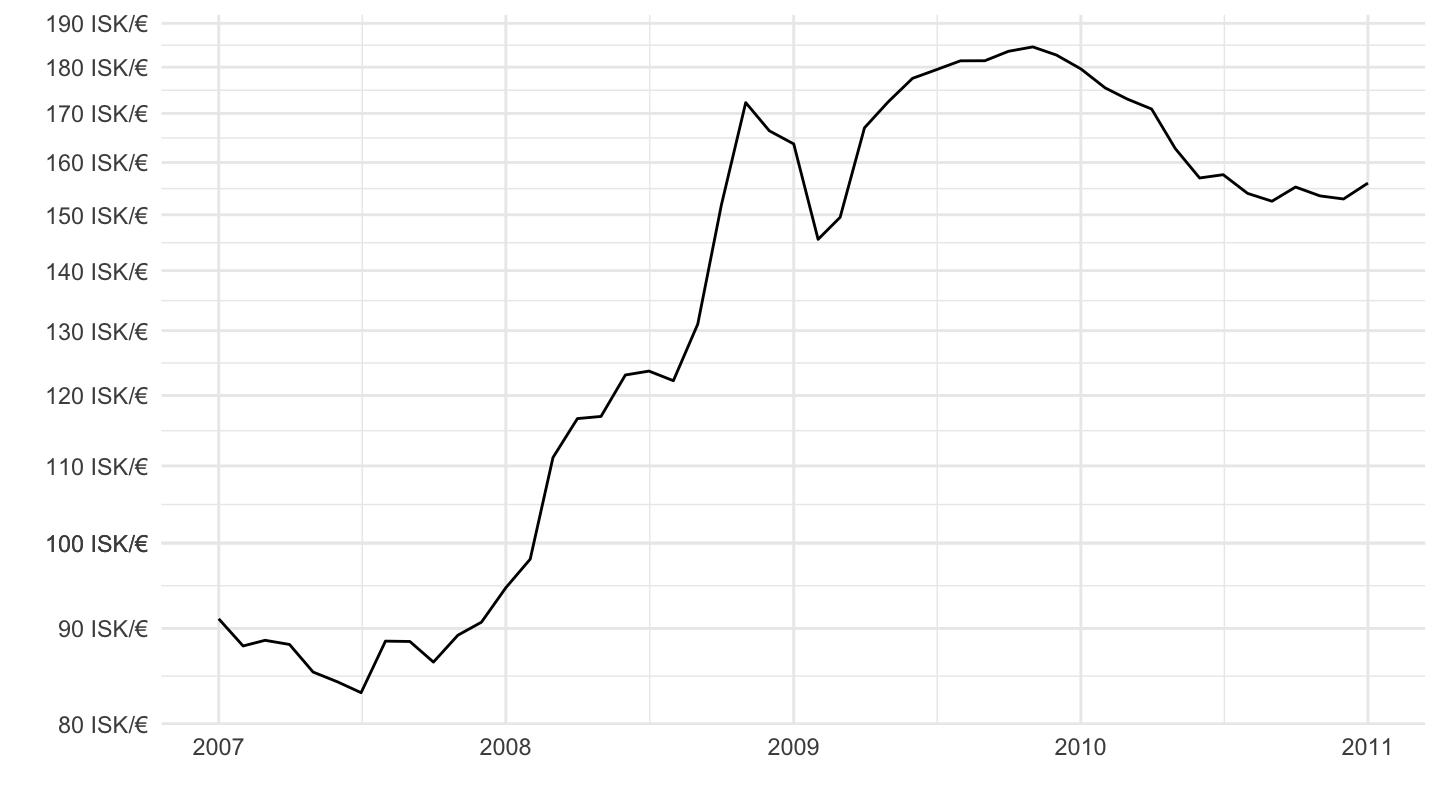
Exchange Rate (2007-2011)
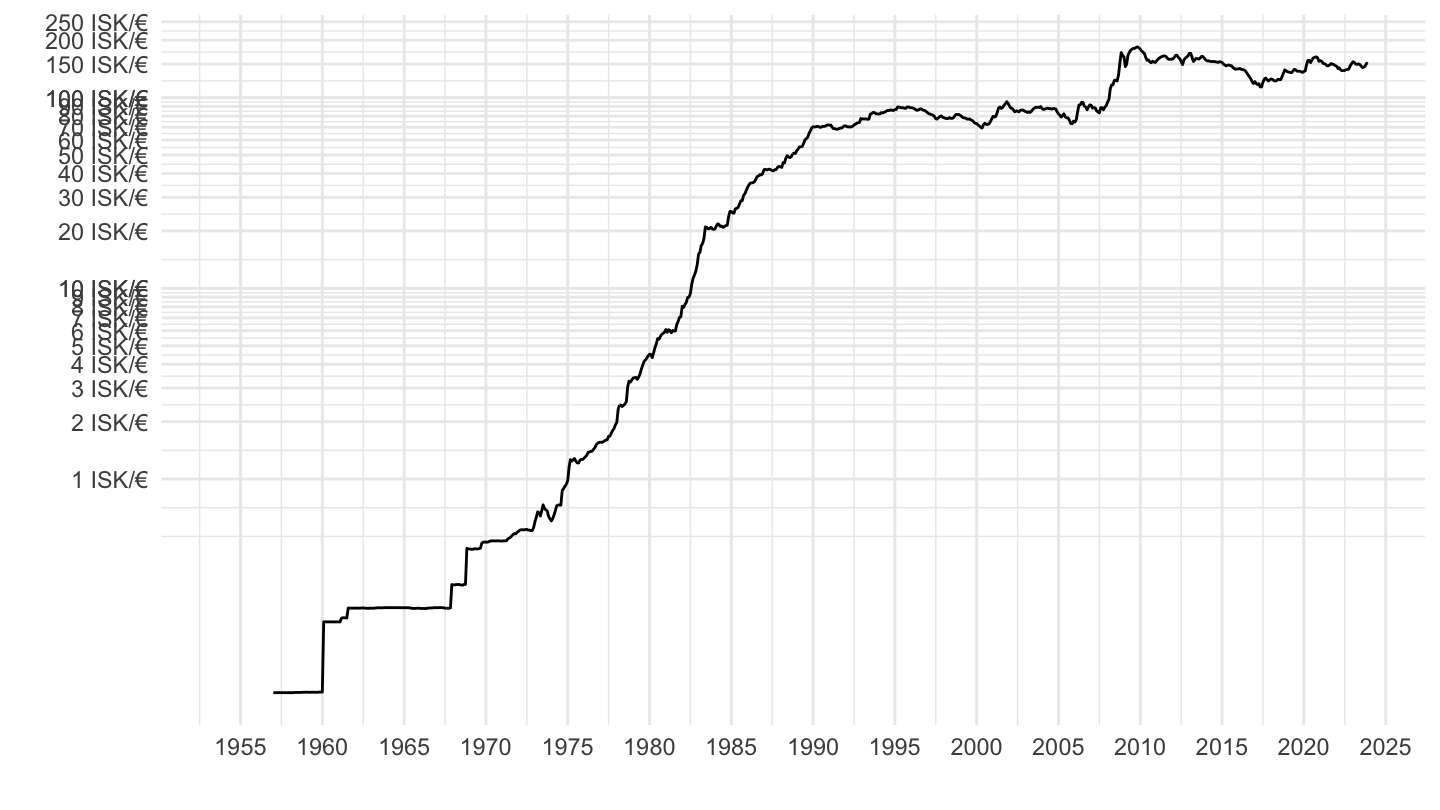
Exchange Rate (Longer)
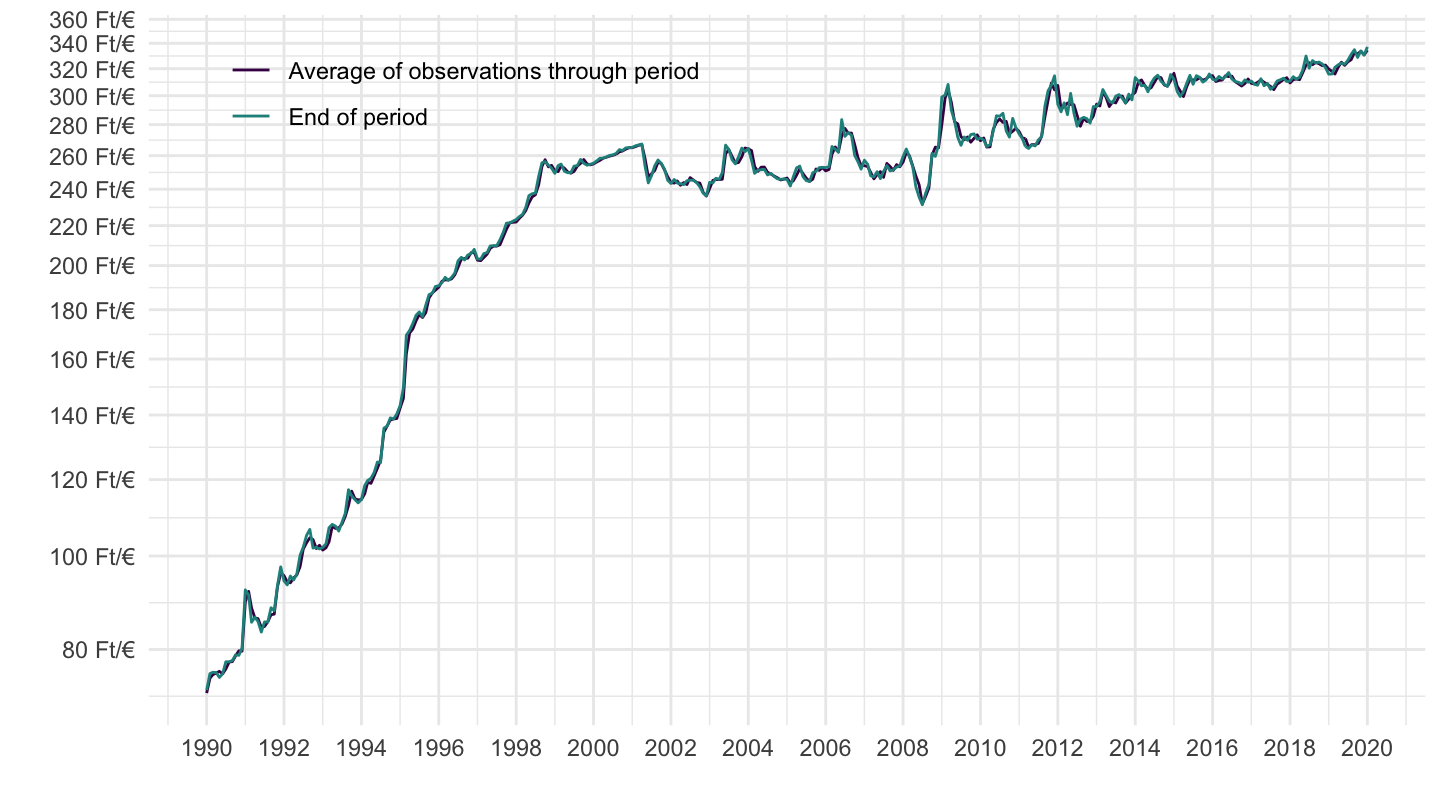
Hungary (1995-2010)
Current Account
Exchange Rates
Current Account

Argentina (1990-2002)
Exchange Rates
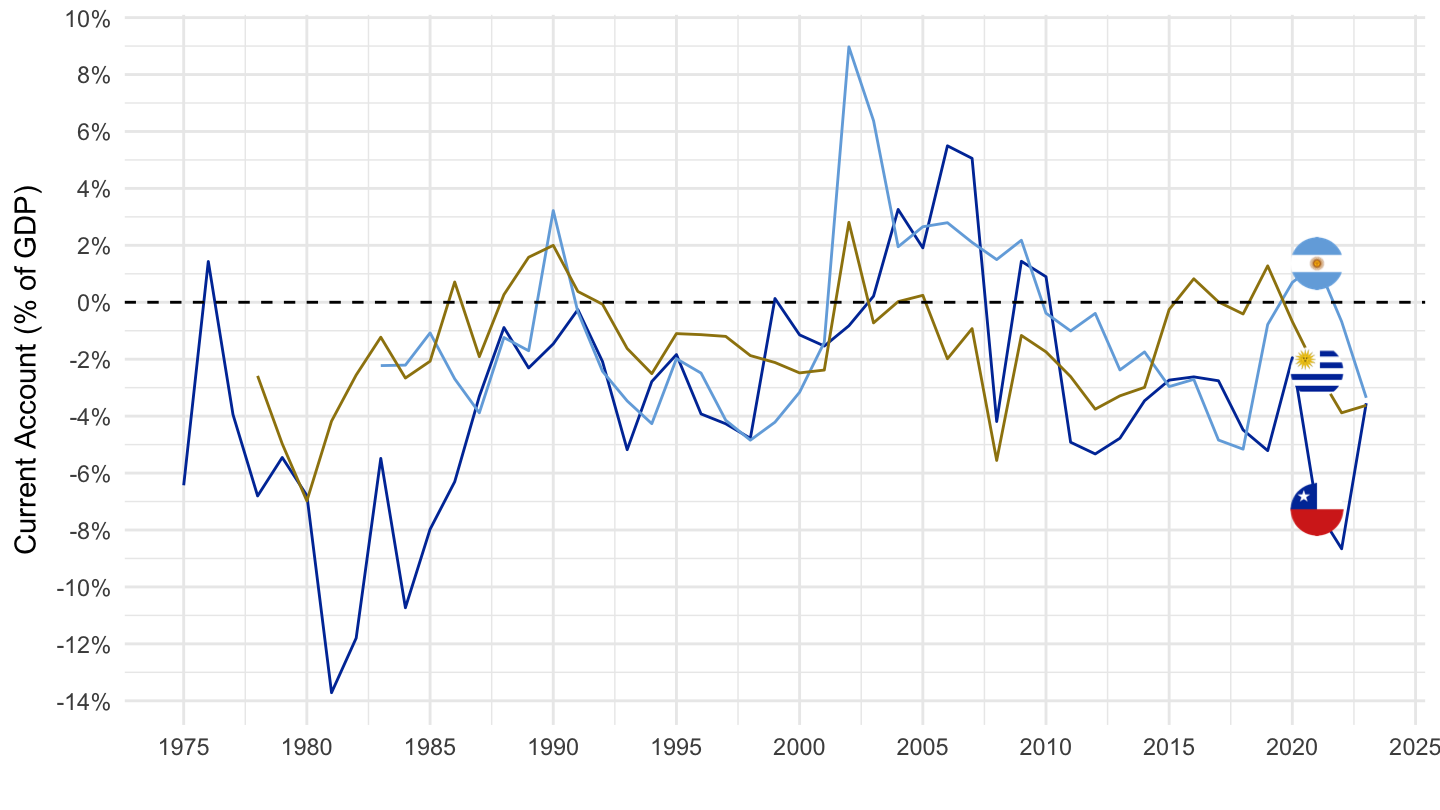
Current Accounts

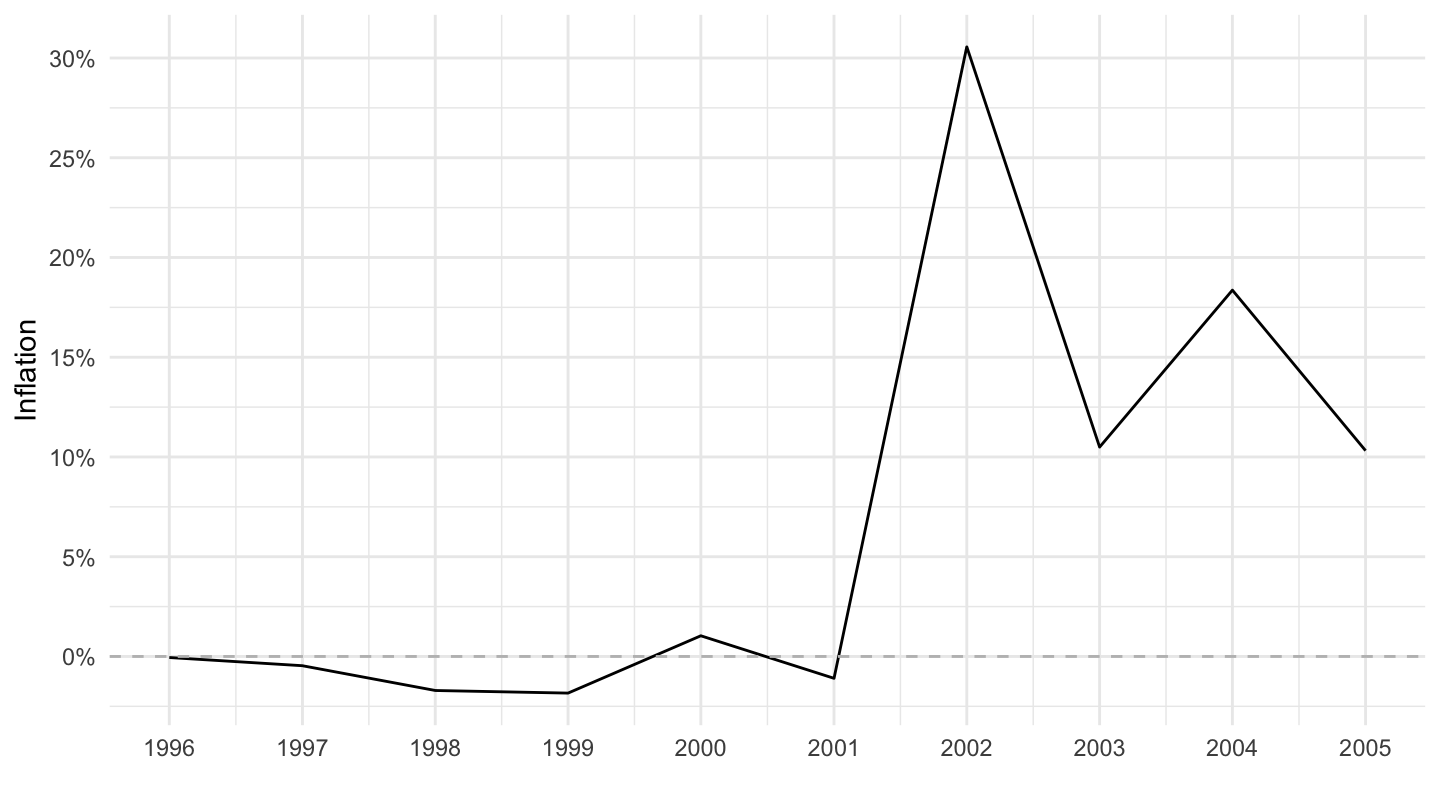
Deflation in Argentina before 2001
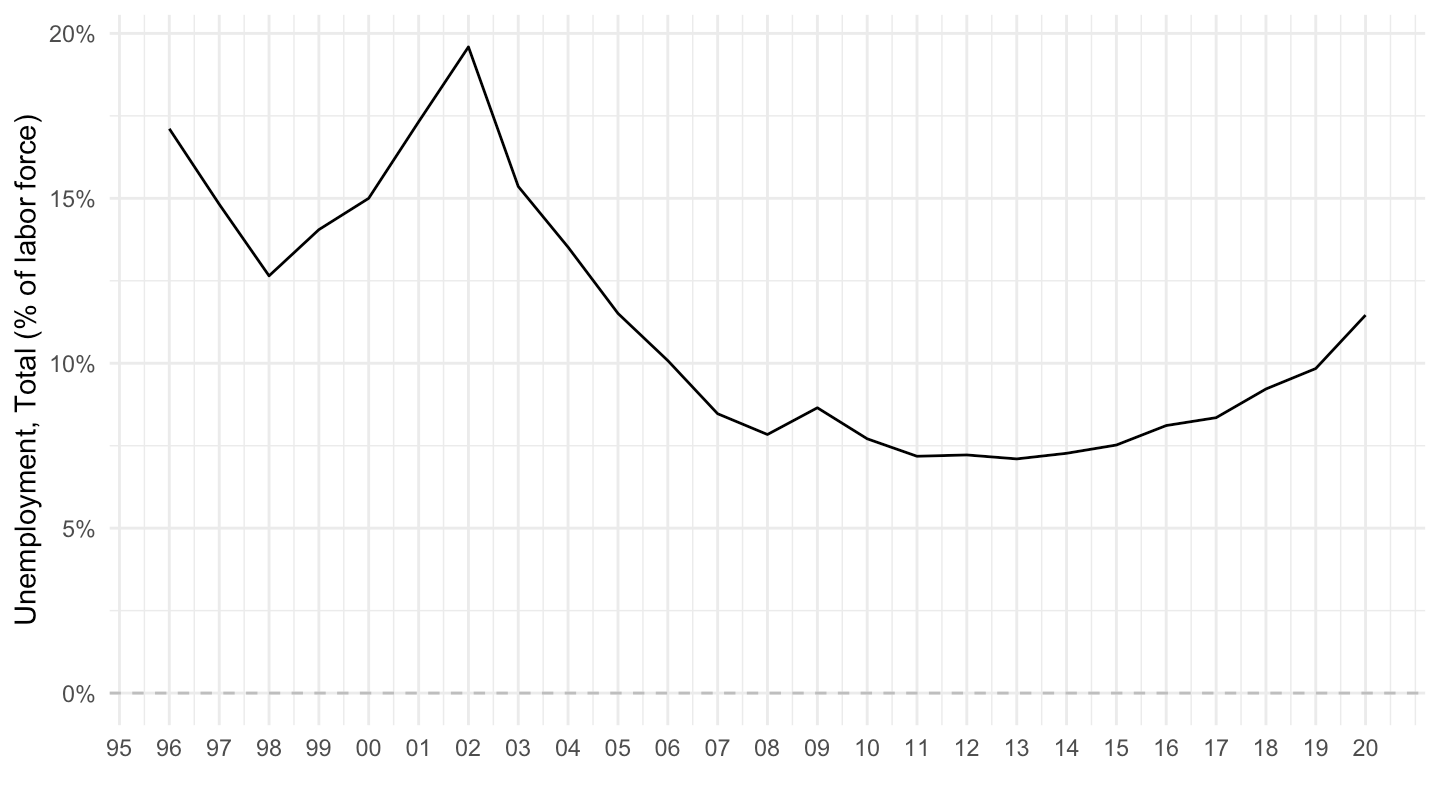
Unemployment in Argentina
Bibliography
Eichengreen, Barry. 1992. Golden Fetters: The Gold Standard and the Great Depression, 1919-1939. Oxford University Press.
Mundell, Robert A. 1961a. “A Theory of Optimum Currency Areas.” The American Economic Review 51 (4): 657–65. https://www.jstor.org/stable/1812792.
———. 1961b. “Flexible Exchange Rates and Employment Policy.” The Canadian Journal of Economics and Political Science / Revue Canadienne d’Economique et de Science Politique 27 (4): 509–17. https://doi.org/10.2307/139437.
———. 1963. “Capital Mobility and Stabilization Policy Under Fixed and Flexible Exchange Rates.” The Canadian Journal of Economics and Political Science / Revue Canadienne d’Economique et de Science Politique 29 (4): 475–85. https://doi.org/10.2307/139336.